A burn is an injury to the skin or other organic tissue primarily caused by heat or due to radiation, radioactivity, electricity, friction or contact with chemicals.
Thermal (heat) burns occur when some or all of the cells in the skin or other tissues are destroyed by:
- hot liquids (scalds)
- hot solids (contact burns), or
- flames (flame burns).(https://www.who.int)
Nursing Diagnosis :
- Fluid volume deficit related to active fluid loss
- Acute pain related to burn injury
- Impaired skin integrity related to open wounds
- Hyperthermia related to dehydration and infection
- Anxiety related to changes in health status
Nursing Interventions
|
No. |
Nursing Diagnosis |
Goal |
Interventions |
|
1. |
Fluid volume deficit related to active fluid loss |
1. Fluid balance Indicator: · Blood pressure within expected range · Balance intake and output in 24 hours · No peripheral edema · No abnormal thirst · Skin hydration · Hematocrit within normal limits 2. Hydration Indicator: · Skin hydration · No peripheral edema · No abnormal thirst · Blood pressure within normal limits · Hematocrit within normal limits 3. Nutritional status: food and fluid intake Indicator: · Oral food intake · Oral fluid intake · Total parenteral nutrition |
Fluid management: 1. Maintain accurate intake and output records 2. Monitor hydration status (moisture of mucous membranes and adequate pulse), if necessary 3. Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes – 1 hour 4. Monitor food/fluid intake and calculate daily calorie intake 5. Collaboration IV fluid administration 6. Monitor nutritional status 7. Give oral fluids Hypovolemic management: 1. Monitor fluid status including fluid intake and output 2. Monitor laboratory results in accordance with fluid retention (BUN, electrolytes, hematocrit, urine osmolality, albumin, and total protein) 3. Monitor the patient's response to fluid additions |
|
2. |
Acute pain related to burn injury |
1. Pain level Indicator: · Reporting pain Duration of pain · Facial expression when in pain · Muscle tension 2. Pain control Indicator: · Recognizing pain · Shows the causal factor · Report changes in pain · Report pain control 3. Degree of discomfort Indicator: · Pain, anxiety · Moaning 4. Vital signs Indicator: · Radial pulse · Respiratory rate · Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure |
Pain Management: 1. Perform a comprehensive pain assessment including location, characteristics, duration, frequency, quality, and precipitating factors 2. Observe nonverbal reactions and discomfort 3. Environmental controls that can affect pain such as room temperature, lighting, and noise 4. Teach about non-pharmacological techniques: deep breathing, relaxation, and distraction. 5. Collaborative administration of analgesics to reduce pain 6. Increase rest 7. Provide information about pain such as the cause of the pain, how long it will take for the pain to subside and anticipated discomfort from the procedure. Analgesic Administration: 1. Determine the location, characteristics, quality and degree of pain before administering the drug 2. Check the doctor's instructions about the type of drug, dosage, and frequency 3. Check allergy history 4. Evaluation of analgesic effectiveness Environmental Management: convenience 1. Determining the source of discomfort 2. Provide a safe and clean environment 3. Facilitate a comfortable patient position |
|
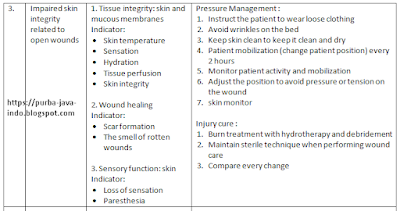
3. |
Impaired skin integrity related to open wounds |
1. Tissue integrity: skin and mucous membranes Indicator: · Skin temperature · Sensation · Hydration · Tissue perfusion · Skin integrity 2. Wound healing Indicator: · Scar formation · The smell of rotten wounds 3. Sensory function: skin Indicator: · Loss of sensation · Paresthesia |
Pressure Management : 1. Instruct the patient to wear loose clothing 2. Avoid wrinkles on the bed 3. Keep skin clean to keep it clean and dry 4. Patient mobilization (change patient position) every 2 hours 5. Monitor patient activity and mobilization 6. Adjust the position to avoid pressure or tension on the wound 7. skin monitor Injury cure : 1. Burn treatment with hydrotherapy and debridement 2. Maintain sterile technique when performing wound care 3. Compare every change |
|
4. |
Hyperthermia related to dehydration and infection |
1. Thermoregulation Indicator: · Report temperature discomfort · Decrease in skin temperature · Skin discoloration, muscle twitching, dehydration 2. Vital signs Indicator: · Body temperature, apical heart rate, apical heart rhythm · Radial pulse. Respiratory rate, breathing rhythm, systolic blood pressure |
Fever management: 1. Monitor temperature as often as possible 2. Monitor skin color and temperature 3. Monitor BP, pulse, RR 4. Give treatment to overcome the cause of fever 5. Improve blood circulation 6. Increase fluid intake and nutrition 7. Leukocyte monitor Monitoring vital signs 1. Monitor presence and quality of pulse 2. Monitor skin tone, temperature and humidity 3. Identify possible causes of changes in vital signs |
|
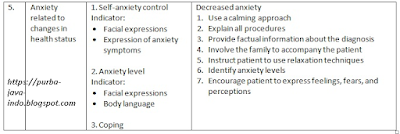
5. |
Anxiety related to changes in health status |
1. Self-anxiety control Indicator: · Facial expressions · Expression of anxiety symptoms 2. Anxiety level Indicator: · Facial expressions · Body language 3. Coping |
Decreased anxiety 1. Use a calming approach 2. Explain all procedures 3. Provide factual information about the diagnosis 4. Involve the family to accompany the patient 5. Instruct patient to use relaxation techniques 6. Identify anxiety levels 7. Encourage patient to express feelings, fears, and perceptions |



0 Comment:
Post a Comment